What kind of difference does numerical output make? [IO-Link compatible] Convenience afforded by the Air Gap Sensor
This blog entry introduces METROL’s IO-Link compatible LK-DPA model in the Air Gap Sensor series of air-type precision seating confirmation sensors.
Table of Contents
IO-Link devices in use around the world
In recent years, there has been a rapid increase in global needs for IO-Link compatible products with communication functions in terminal devices such as sensors. Elsewhere, people unfamiliar with IO-Link may find it difficult to picture the advantages of connecting sensors to a network and the methods of their use.
This article proposes new methods of use for people already using Air Gap Sensors and assists those considering implementing them with product selection. Don’t miss a word.
What you can learn from this blog article
・ Features of the IO-Link compatible Air Gap Sensor LK-DPA
・ How to actually use the LK-DPA
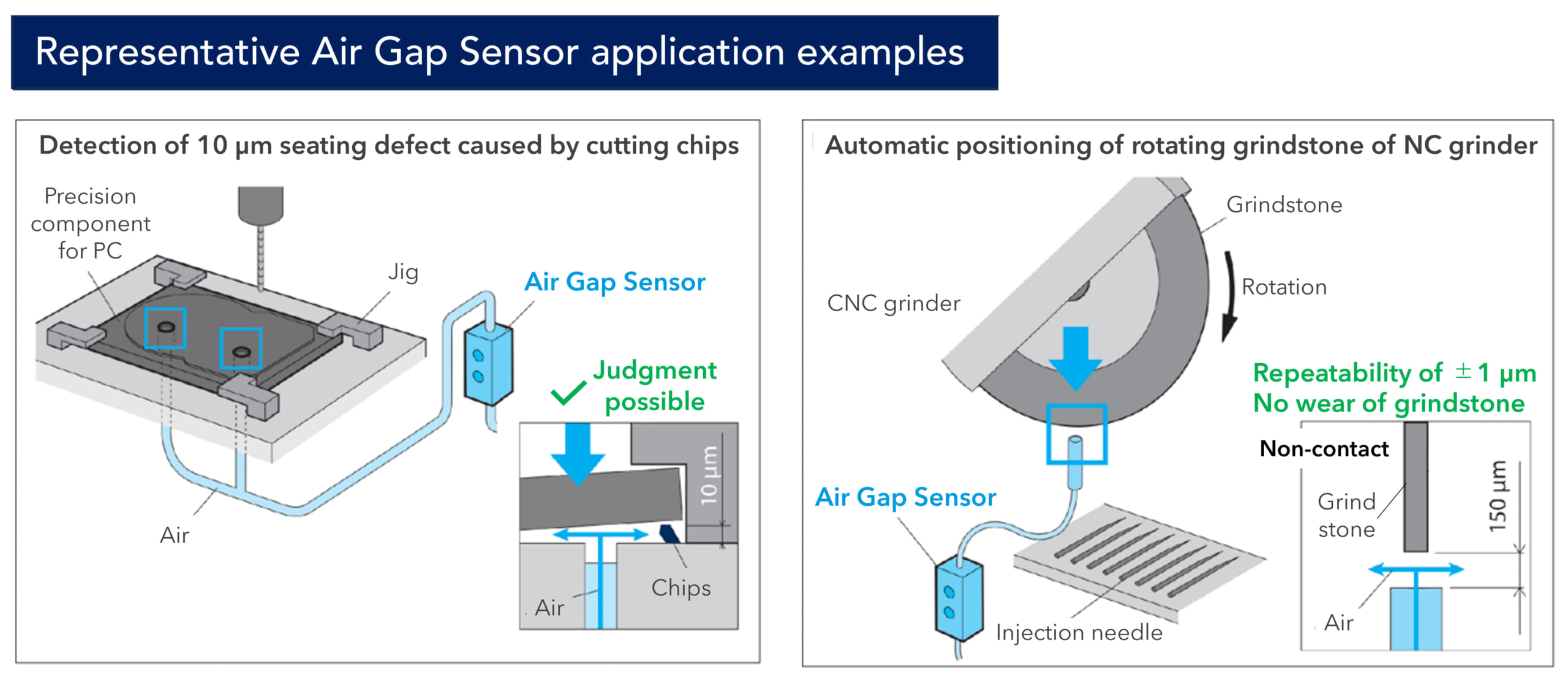
Air Gap Sensor Overview
Before starting on the main topic, here is an overview of MEROL’s Air Gap Sensor series of air-type precision seating sensors.
Adhesion Confirmation Between The Workpiece And The Jig
Air Gap Sensors are sensors that use the change in air pressure to sense gaps.
The series includes
- IO-Link compatible types
- IO-Link non-compatible types
With the same basic structure and applications, they are mainly used for “adhesion confirmation”, making sure the workpiece is set on the jig without a gap during machining.
While the air sensors of most other manufacturers have a precision of no less than 5 μm, METROL’s Air Gap Sensors offer a high precision of ±0.5 μm. Because they can definitively detect workpiece “floating” on a micron scale, caused by cutting chips between the workpiece and the jig during seating, they are used on production lines where precision machining is required, such as automotive brake parts and HDDs.
Air gap sensors are not only used for “workpiece seating confirmation”. There are various applications that utilize the high accuracy of the sensor, such as
・Position detection of grinder rotating grind stone and
・Inner diameter judgment of cylindrical workpieces
What Is The IO-Link Compatible Air Gap Sensor LK-DPA?
Here we will go into detail about the IO-Link compatible LK-DPA model within the Air Gap Sensor series.
Realizing predictive maintenance and traceability with air pressure numerical output
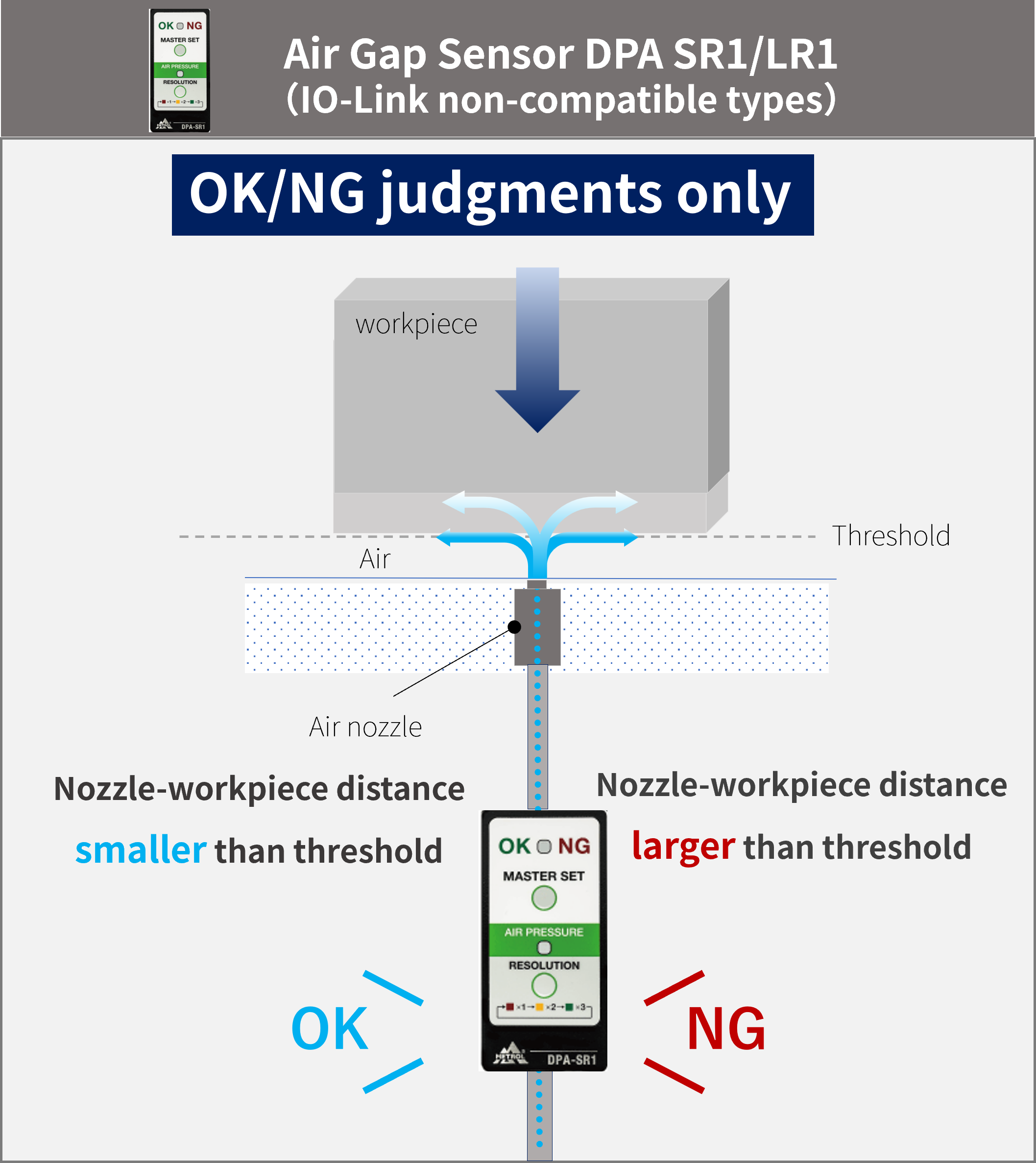
The main feature of the LK-DPA is its ability to acquire pressure values as numerical data.
While conventional models offered only OK/NG judgments based on master values, use of the LK-DPA makes it possible to display detected values in real time and record them as data. This also enables support for predictive maintenance and traceability (the mechanism that allows tracing of the product manufacturing process).
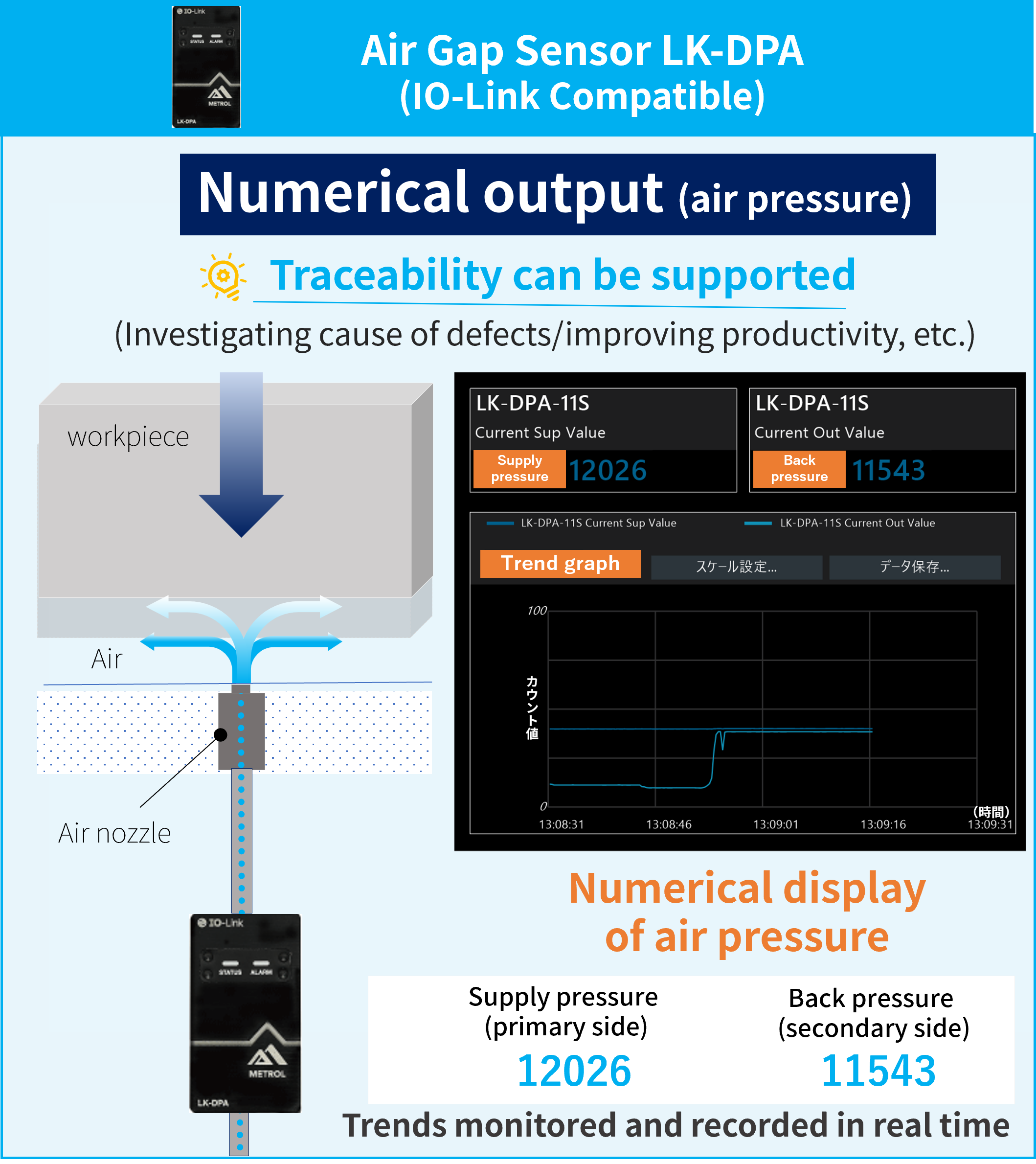
Visualizing numerical values helps find problems faster
Using the air pressure value data, defects such as flow path air or nozzle clogging can be identified earlier. Problems bringing production to a stop can be headed off, maintaining high operating rates.
If a defect arises, rendering when, where, and how it occurred traceable is now an essential function in fields such as the automotive industry where safety standards are stringent. The LK-DPA supports these needs.
Also, gaps usable with higher repeatability can be set as threshold values, improving precision and productivity.
How air pressure value data acquired with IO-Link can be used
- Grind stone gap amount value calculation
- Earlier identification of defect causes based on numerical data (air nozzle clogging due to cutting chips, piping air leaks, etc.)
- Improved precision and productivity through threshold value setting for high-repeatability gaps, etc.
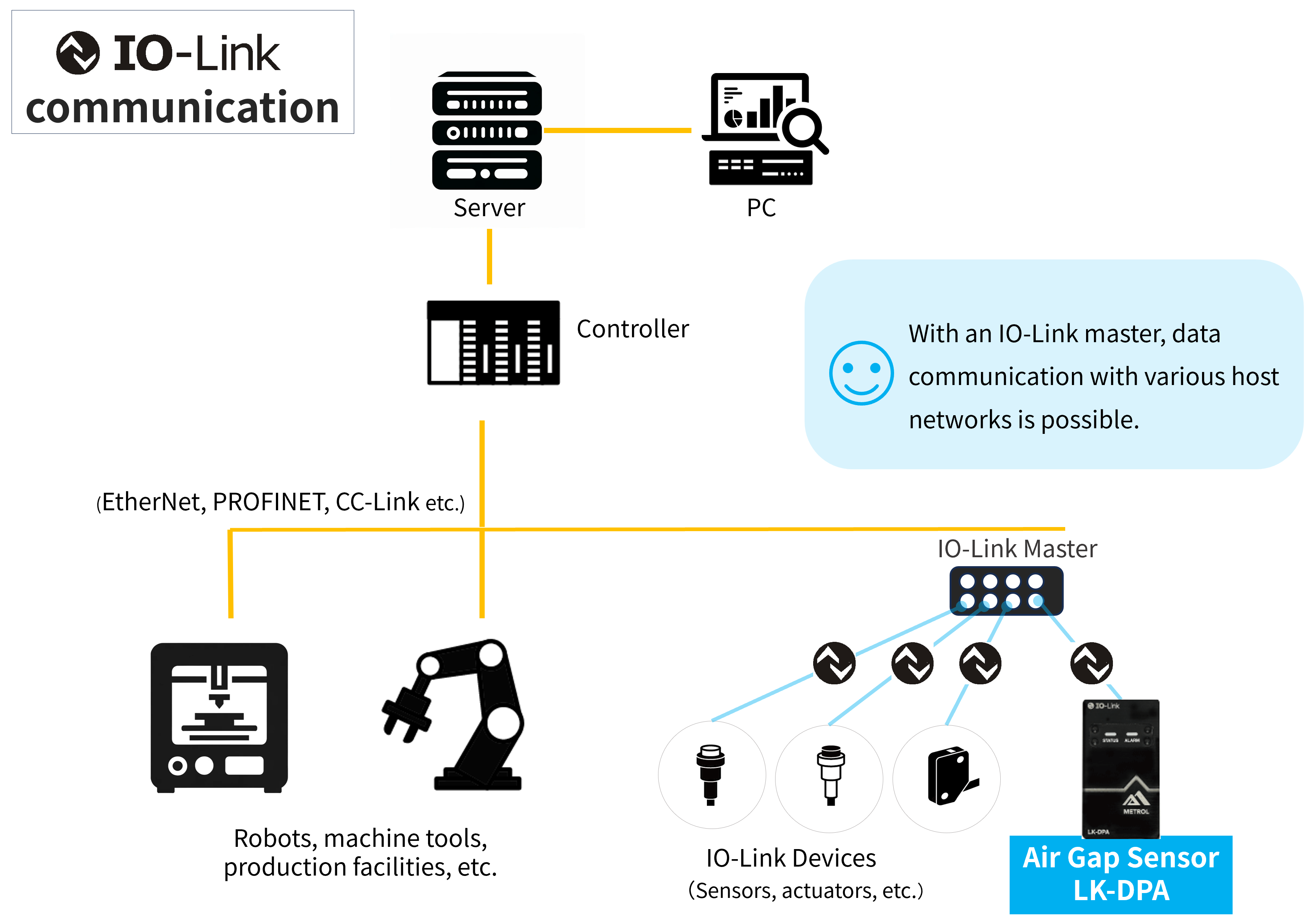
Highly versatile and convenient communication standard IO-Link adopted
LK-DPA uses IO-Link as the digital communication standard for connection with the controller.
While IO-Link is a relatively new communication standard, it has received user support due to
- Versatility enabling integration with all fieldbuses and networks
- Convenience enabling easy connection with standard sensor cables
In recent years it has become rapidly accepted in markets around the world.
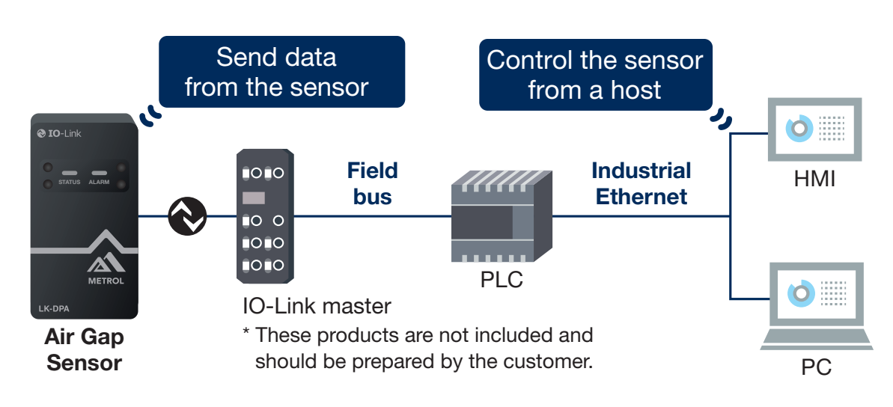
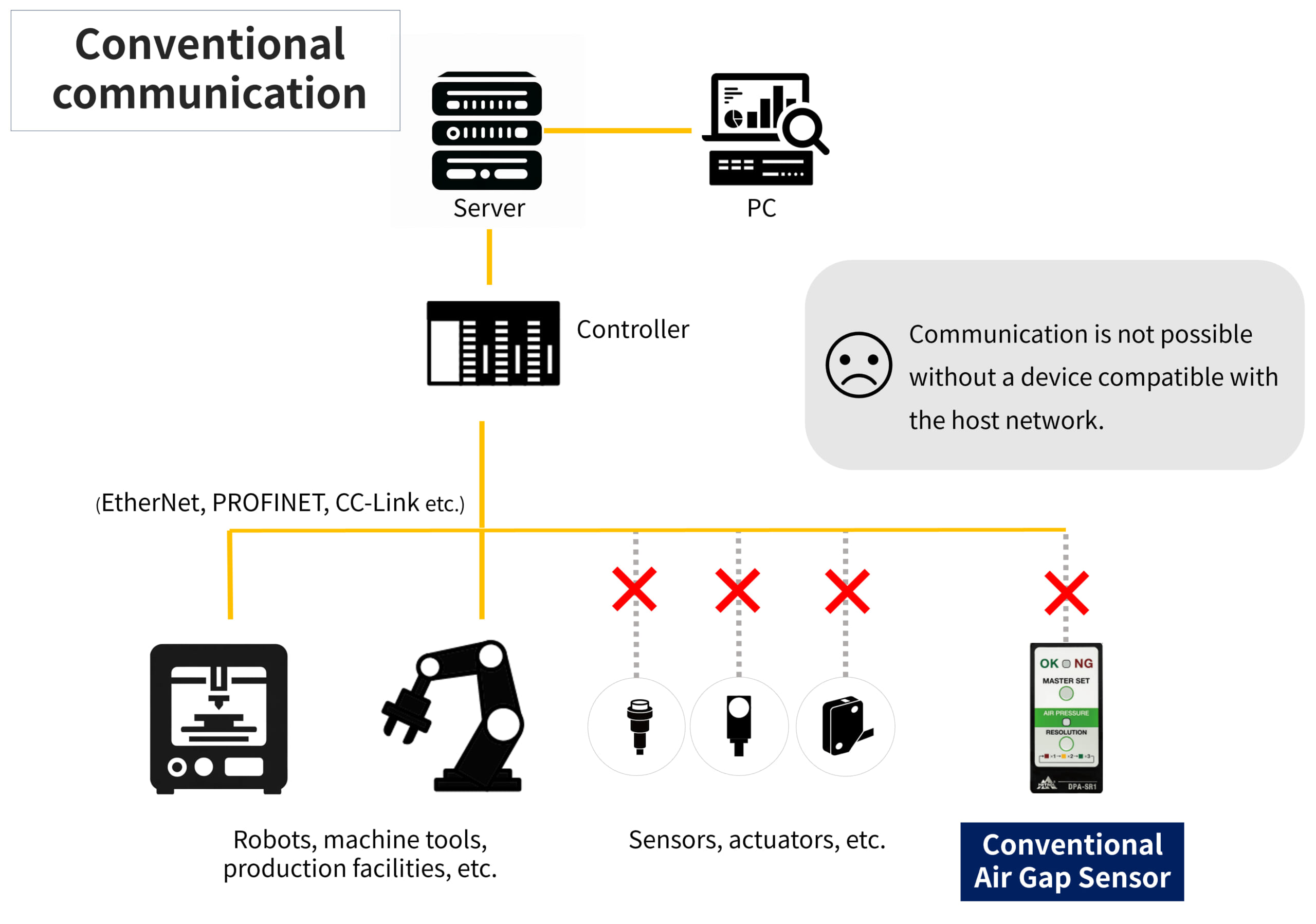
IO-Link master
The use of IO-Link requires an IO-Link master device for connecting the device to the host network, which is compatible with general industrial networks (PROFINET, EtherNet/IP, EtherCAT, etc.). Therefore, additional wiring or reconstruction are not required even if a host network is already in use.
One IO-Link master can connect 4 to 16 devices, and you can just plug in the cable for data communication to start automatically. Users find this easy connection a great convenience.
[Demo introduction] Easy connection. Usage of the IO-Link compatible LK-DPA
Here we will discuss how to connect the LK-DPA to IO-Link, showing the actual process with a demo model.
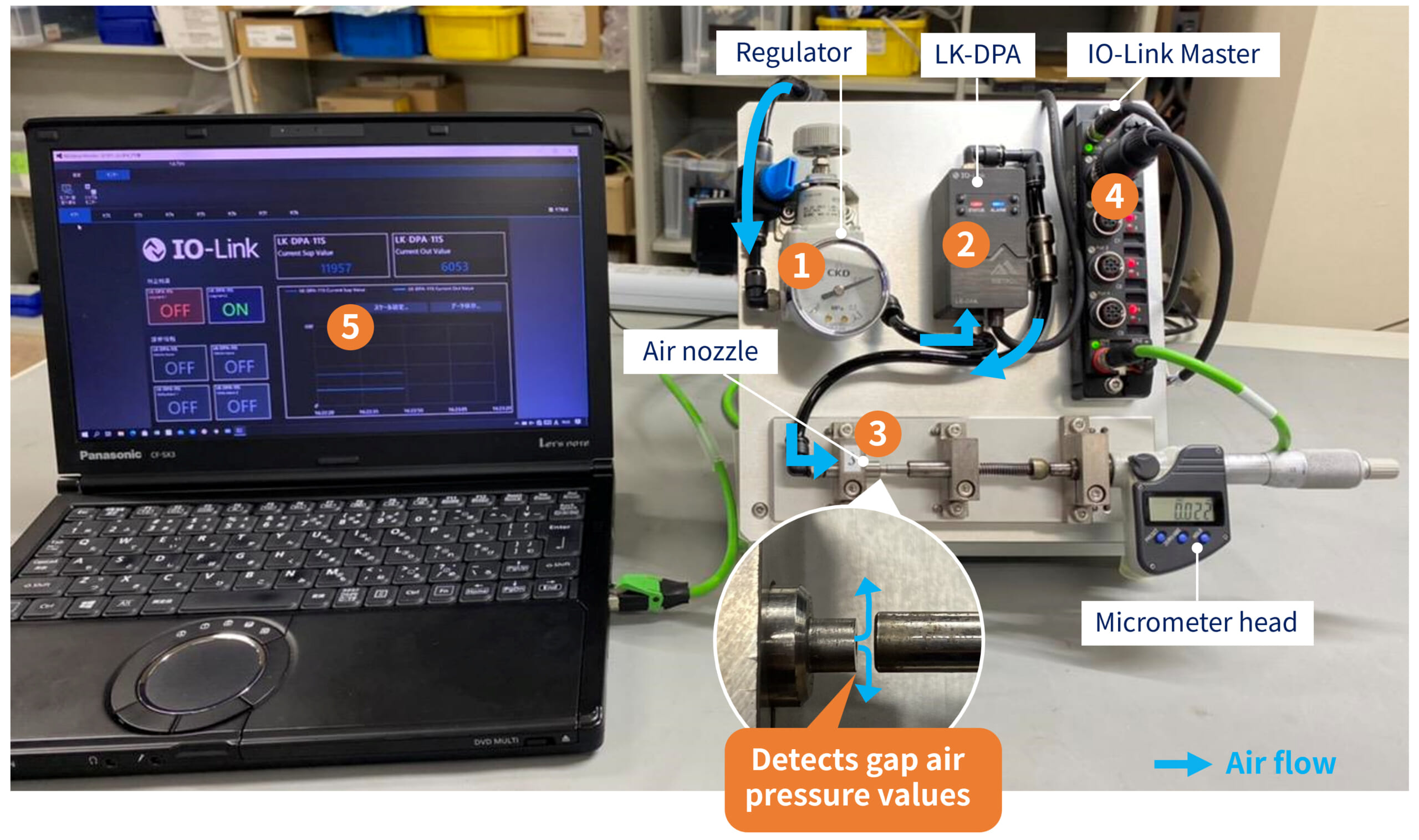
The demo model structure is as below.
Components used in demo model *See Figure 1
- Precision regulator: Regulates compressed air pressure and keeps it constant
- LK-DPA: IO-Link compatible Air Gap Sensor (METROL product)
- Air nozzle: Supplies air
- IO-Link master: Interpreter connecting IO-Link device and host network
(Included with 3.) Micrometer head: Used instead of a workpiece to digitize gap amount - PC for data display: (Keyence app is used here.)
Air supplied from the compressor
Step 1:Passes through ① precision regulator and ② LK-DPA to be emitted from ③ air nozzle.
Step 2: LK-DPA detects the air pressure values which change with the gap distance between ③ air nozzle and the micrometer (workpiece in actual use).
Step 3: Detected air pressure value data passes through ④ IO-Link master to be displayed on ⑤ PC.
IO-Link connection can be done in 3 easy steps
Step 1: Connect IO-Link master power cable
Step 2: Connect LK-DPA and IO-Link master
Step 3: Connect IO-Link master to Ethernet
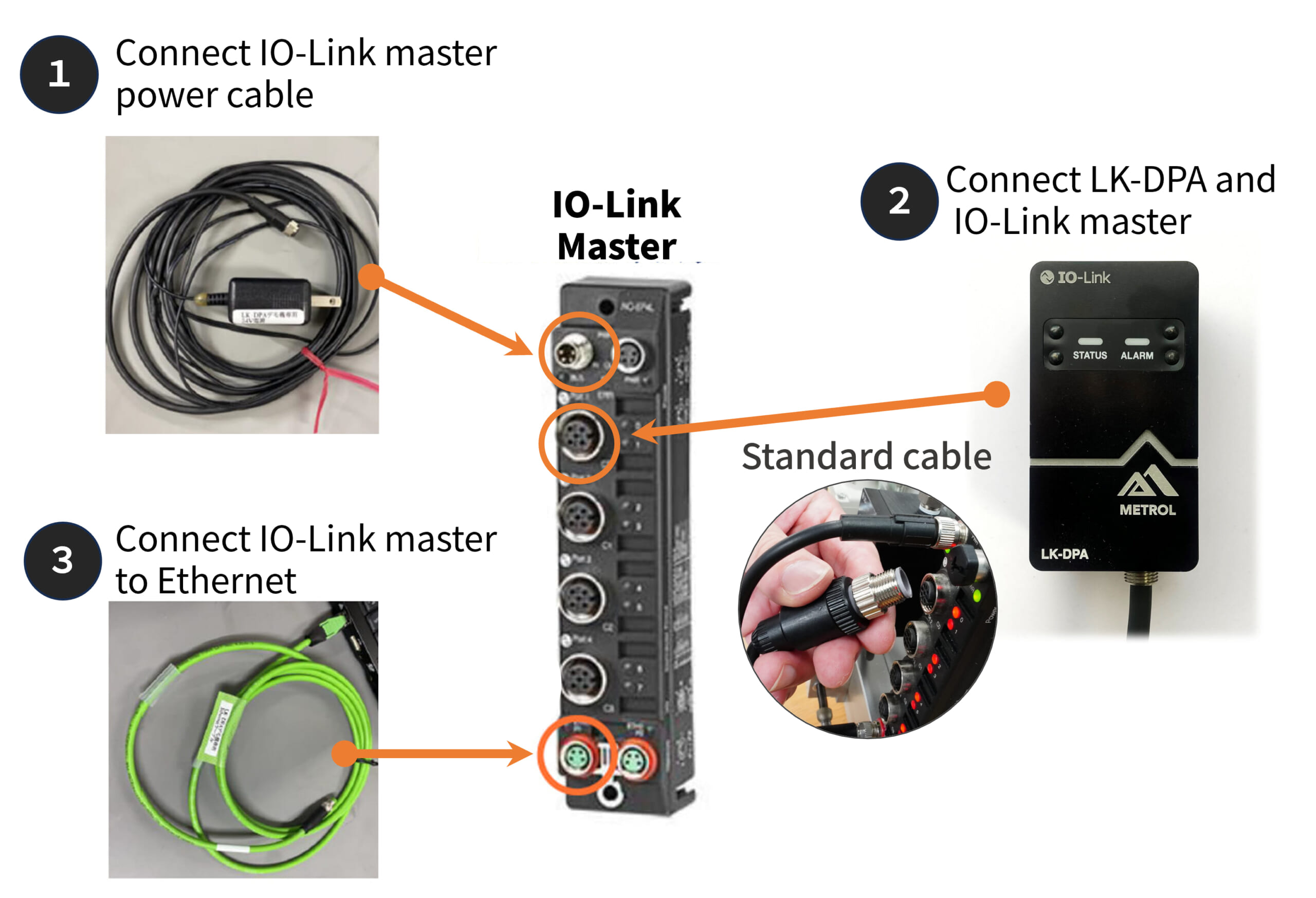
As in Figure 2, just connect the cable to the IO-Link master to begin IO-Link communication.*
(*Upon initial connection, Ethernet connection setting between the IO-Link master and the PC is required.)
The connected PC monitor will show the following information. (Display content created with Keyence app)
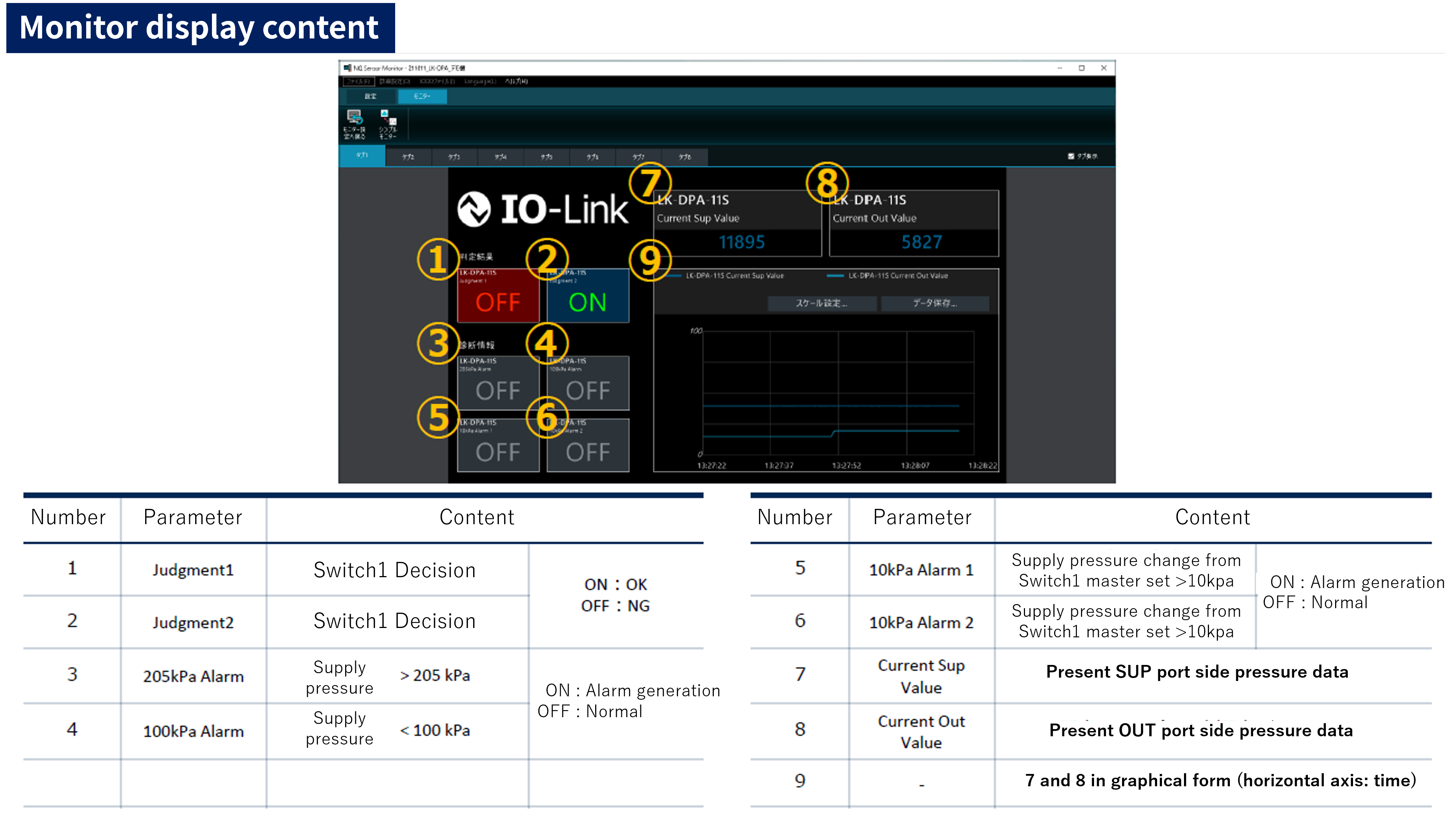
[Reference Video] When using the LK-DPA, numerical values are displayed in this way on the PC screen.
See how the numerical data detected with the LK-DPA when the distance (gap) between the nozzle and the workpiece is changed is actually displayed on the PC screen. Air pressure value trends can be confirmed in real time.
Advantages beyond IO-Link to choosing the LK-DPA
The LK-DPA is not just IO-Link compatible and capable of providing numerical output, it also has the following advantages.
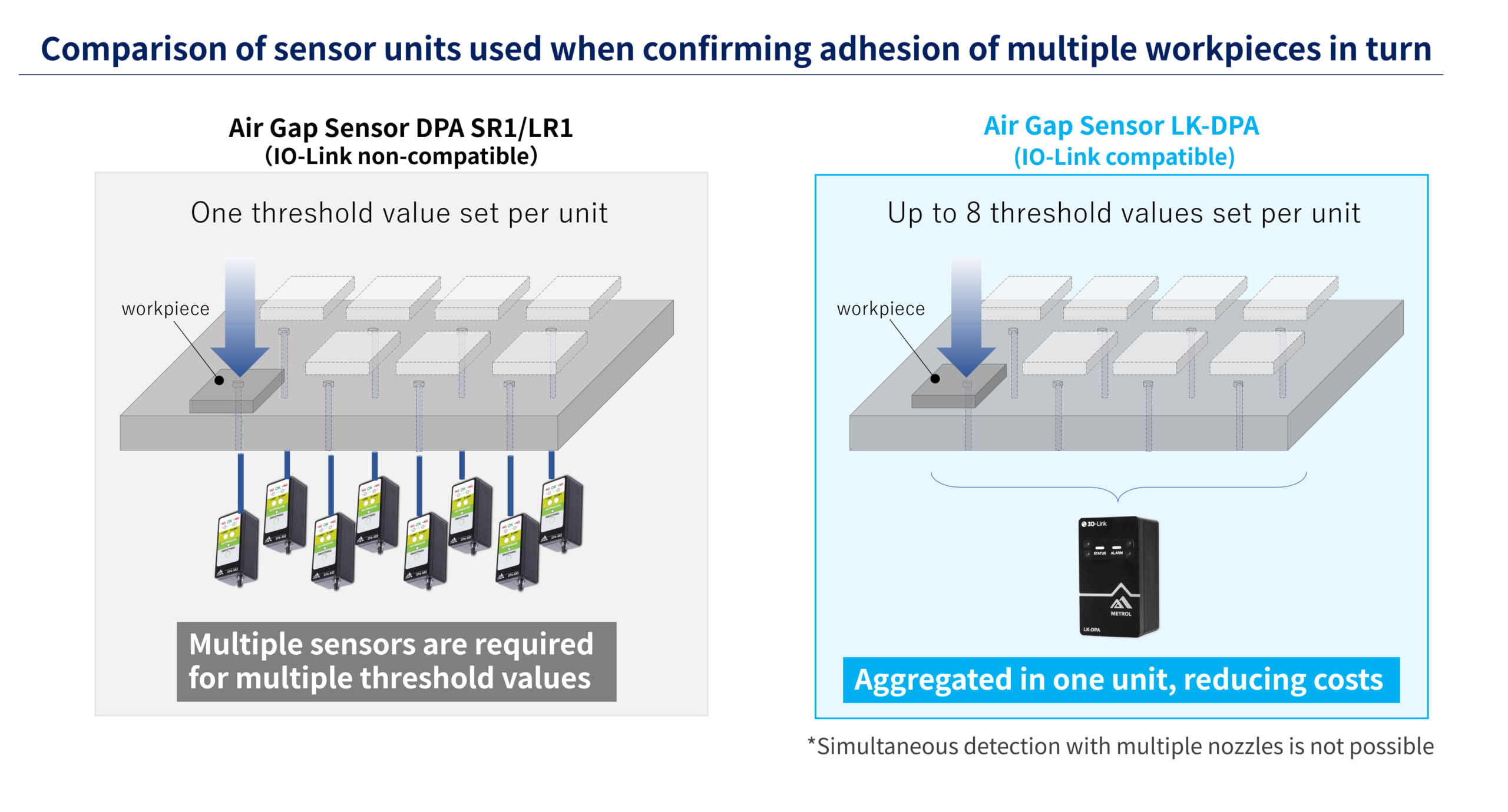
Up to 8 threshold values can be set, reducing costs
The LK-DPA enables up to 8 threshold values to be set.
Compared to its series counterparts, which allow only 1 to 3 threshold values, the LK-DPA can aggregate up to 8 values in one unit, reducing sensor purchasing costs when multiple threshold values are required.
With the IO-Link connection, there is also no need to worry about extra trouble with setting or maintenance accompanying increased threshold values. Because IO-Link has a data storage function, there is no trouble with maintenance or replacement.
Compact body which fits into small machines
The LK-DPA has a compact body just two-thirds the size of its DPA series counterparts, saving space. It also contributes to miniaturization of the machine on which it is mounted.

Examples of user applications
Below are examples of applications of the Air Gap Sensor LK-DPA.
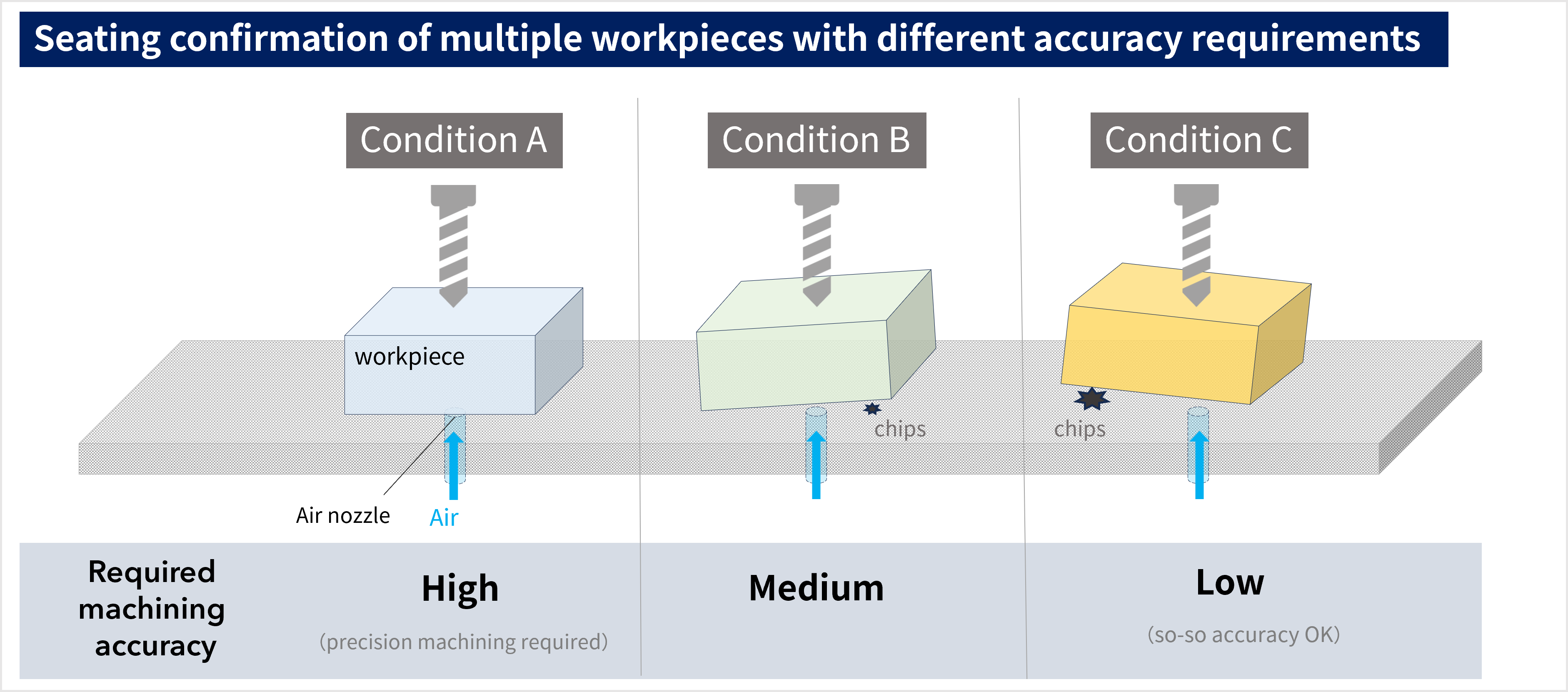
Example 1: Seating confirmation of multiple workpieces with different accuracy requirements
In this example, the Air Gap Sensor is used to confirm that the workpiece is tightly seated on the jig before cutting.
Here, in order to increase the yield rate, the user wanted to set multiple seating levels for different conditions, from condition A (high machining accuracy is required) to condition C (so-so machining accuracy is sufficient).
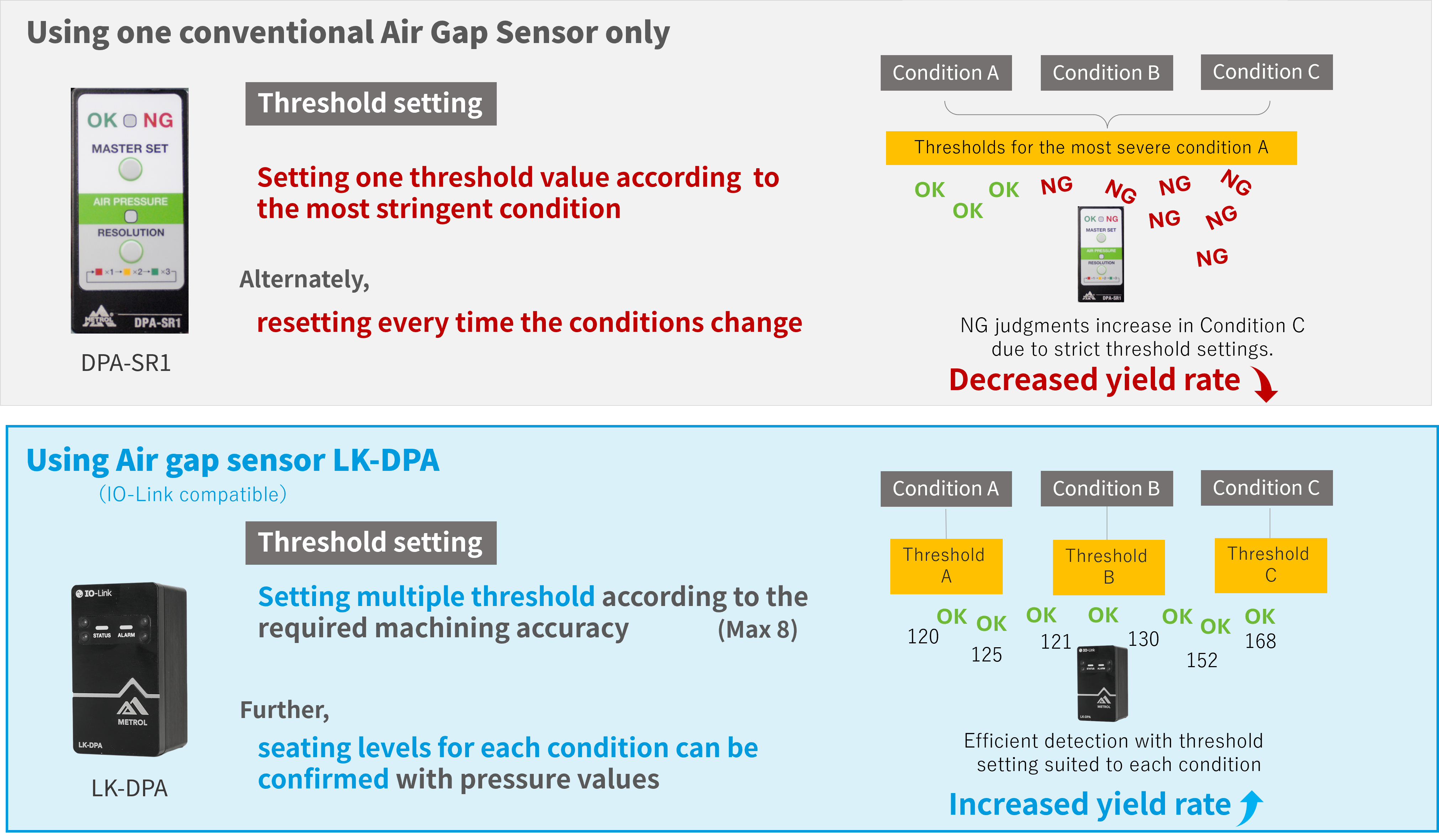
Conventional sensor
Because conventional Air Gap Sensors cannot have multiple thresholds, it is impossible to differentiate the stringency of seating conditions. Therefore, when using a common threshold, it had to be set to the most stringent condition. As a result, productivity for workpieces with lower accuracy requirements remained low.
To improve this, resetting of threshold values was required each time the conditions changed, which added more steps to the process.
LK-DPA
On the other hand, because the LK-DPA can have up to 8 threshold values, multiple values can be set according to the required machining accuracy. In addition, it becomes possible to confirm in detail the seating levels with pressure values.
Setting staged threshold values makes it possible to reduce NG judgments for workpieces with low required machining accuracy, increasing the overall yield rate.
Example 2: Inner diameter judgment of cylindrical workpieces
In this example, the LK-DPA is used for inner diameter judgment of cylindrical workpieces.
Air is emitted from a nozzle set inside the cylindrical workpiece, using its pressure value to judge whether the inner diameter has been machined to the specified size.
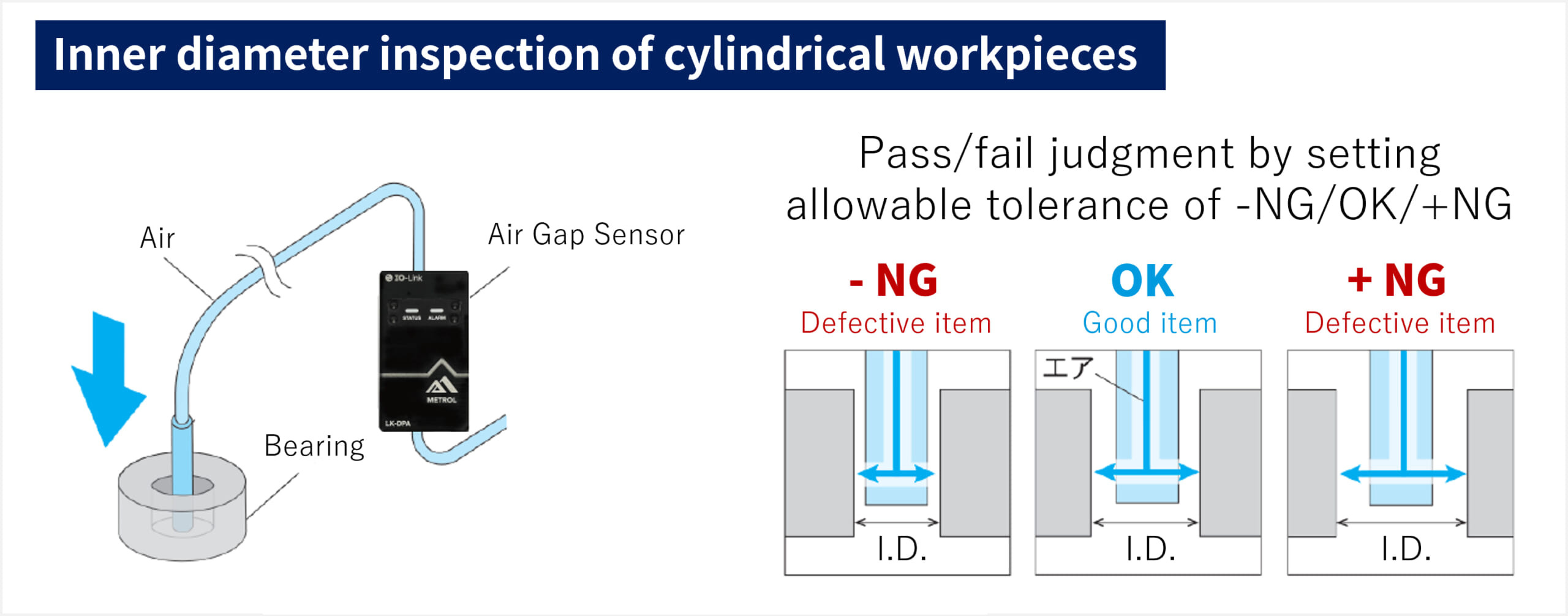
Conventional sensor
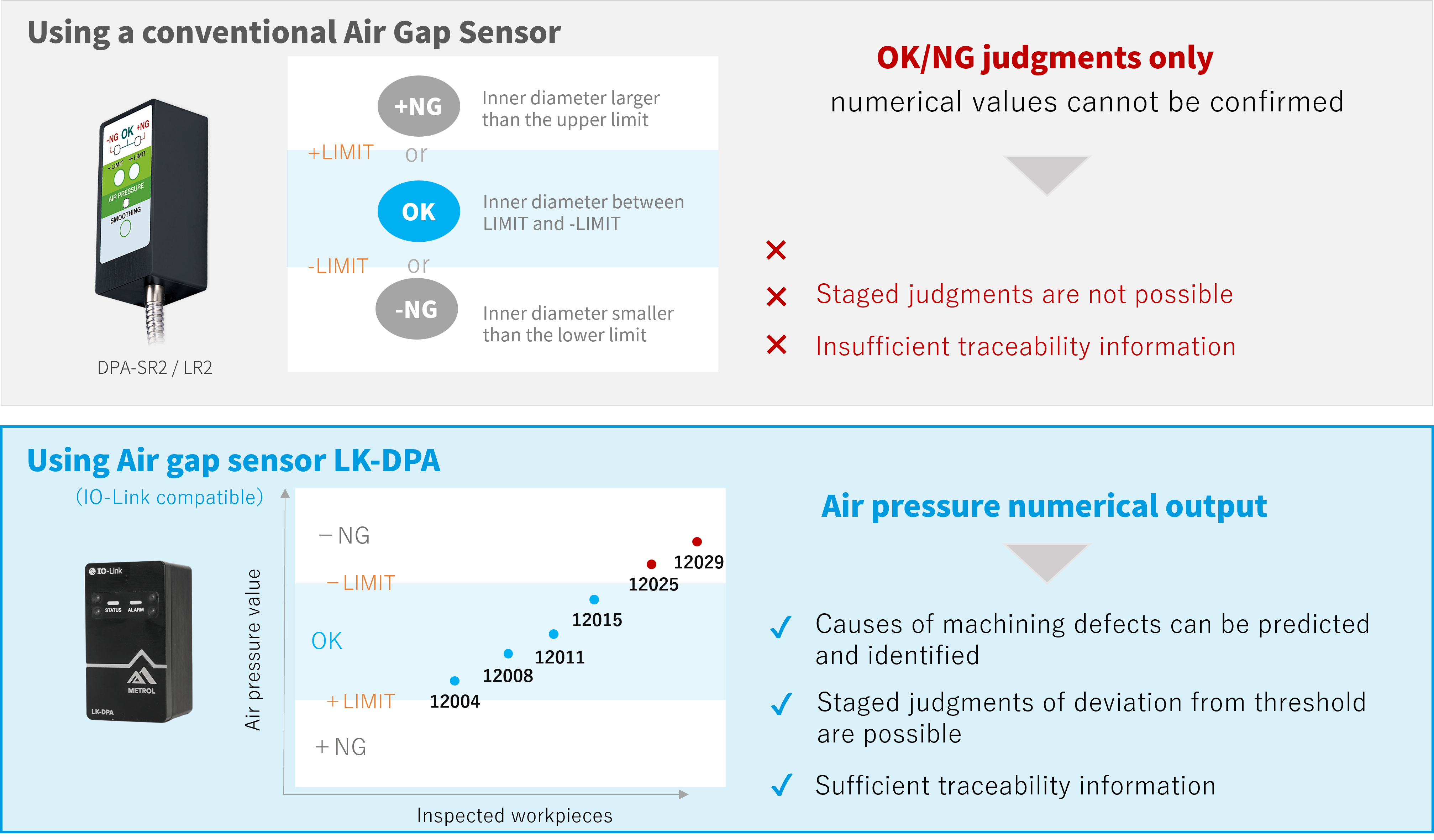
Conventional Air Gap Sensors can only provide judgments of +NG, OK, and -NG, without elucidating the process leading to the OK/NG judgment.
LK-DPA
Because the LK-DPA has numerical output, it is possible to monitor the trends of air pressure as well.
Using this data, machining defect causes can be estimated.
For example,
・ Workpieces machined later have increasingly high air pressure, finally reaching a -NG judgment
→ What is the likely cause of machining defect? : Tool wear
・ Although the air pressure values were stable, they shot up suddenly after a given workpiece, resulting in -NG judgments
→ What is the likely cause of machining defect? : Tool deformation or breakage
Also, analysis of the recorded values can detect machine malfunctions before they lead to machining defects, mainly contributing to
・ Maintenance of operating rate and productivity
・ Reduced losses of time and material costs
In addition, the Air Gap Sensor LK-DPA is used for various applications in a wide range of industries, such as monitoring of gap change amounts in POC (proof of concept testing) equipment.
Find the product introduced in this article here
[IO-Link Compatible] Air Gap Sensor LK-DPA
Ideal for IO-Link compatible equipment
First IO-Link compatible model in the series. Visualizes the production process through constant monitoring, remote management and predictive maintenance based on aggregated data. Combined with an IO-Link master, sensor internal data can be sent to and from PLCs and networks.
![[IO-Link Compatible] Air Gap Sensor LK-DPA](https://metrol-sensor.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/03/img_products_air_gap_sensor_lk-dpa-400x400.png)
